Search results page feature overview
A search results page is much more than a list of links. Funnelback provides a rich set of functionality that assists you to find what you are looking for.
This starts with the search box. Funnelback supports both simple and advanced searches, with auto-completion assisting the user as soon as they begin typing.
Once a search has been submitted, a set of search results will be produced by looking up the words in the search index. The search results are enriched with a host of additional features that can be used to maximize the search experience.
Search box
Simple search form

The search box is the means by which most users interact with a search engine.
A question is asked by typing a few words into the search box and clicking the search button or pressing enter.
This question is then processed by the search engine and a list of results returned to the user.
Search boxes have become simpler over the years now mostly being a single input field and submit button. However, the level of functionality provided by the search box has increased despite the search box becoming simpler.
A lot of things happen behind the scenes when interacting with a modern search box - this can include things like expanding a user’s query with synonyms, or using information that is known about the user’s current location.
This has led to users having high expectations of the quality of what is returned by a search engine, even when minimal information is provided. Most users input single word queries, yet search engines are still able to deliver results that are relevant to the user.
Advanced search form
Advanced search forms were very common in the past - they provide users with lots of fields that allow for very specific searches to be defined by a user. However, they have disappeared from searches as simple search boxes have become smarter to the point where they are quite rare nowadays.
Funnelback has support for advanced search forms but the practical use for an advanced search form has diminished to the point where they are only suitable for very specific audiences such as librarians or legal professionals who have a long history of using advanced search.
It is a common misconception that advanced search will provide the user with better results. In fact studies have found that in most cases users of advanced search yield poorer results because the complexity of the search form means the user doesn’t really understand how to use the form, thus specifying queries that are suboptimal, or queries that don’t make sense.
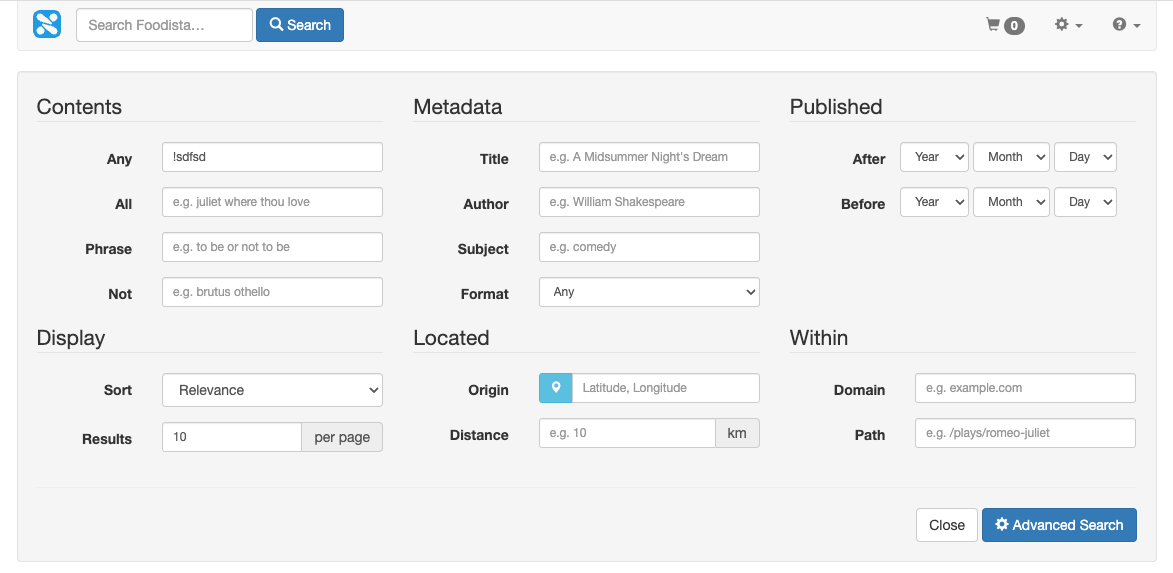
The advanced search form can be fully customized.
The location of an advanced search feature using Funnelback will vary with each implementation, but will often look similar to the following:
Auto-completion
Auto-completion provides the user with real-time suggestions as search terms are typed into the search box. Funnelback supports several forms of auto-completion.
The different types of auto-completion can be combined so that suggestions are returned from multiple auto-completion sources
Simple auto-completion
As the user begins to type a search keyword or phrase, the search box presents the user a list of suggestions that predict what the user might want. For example:
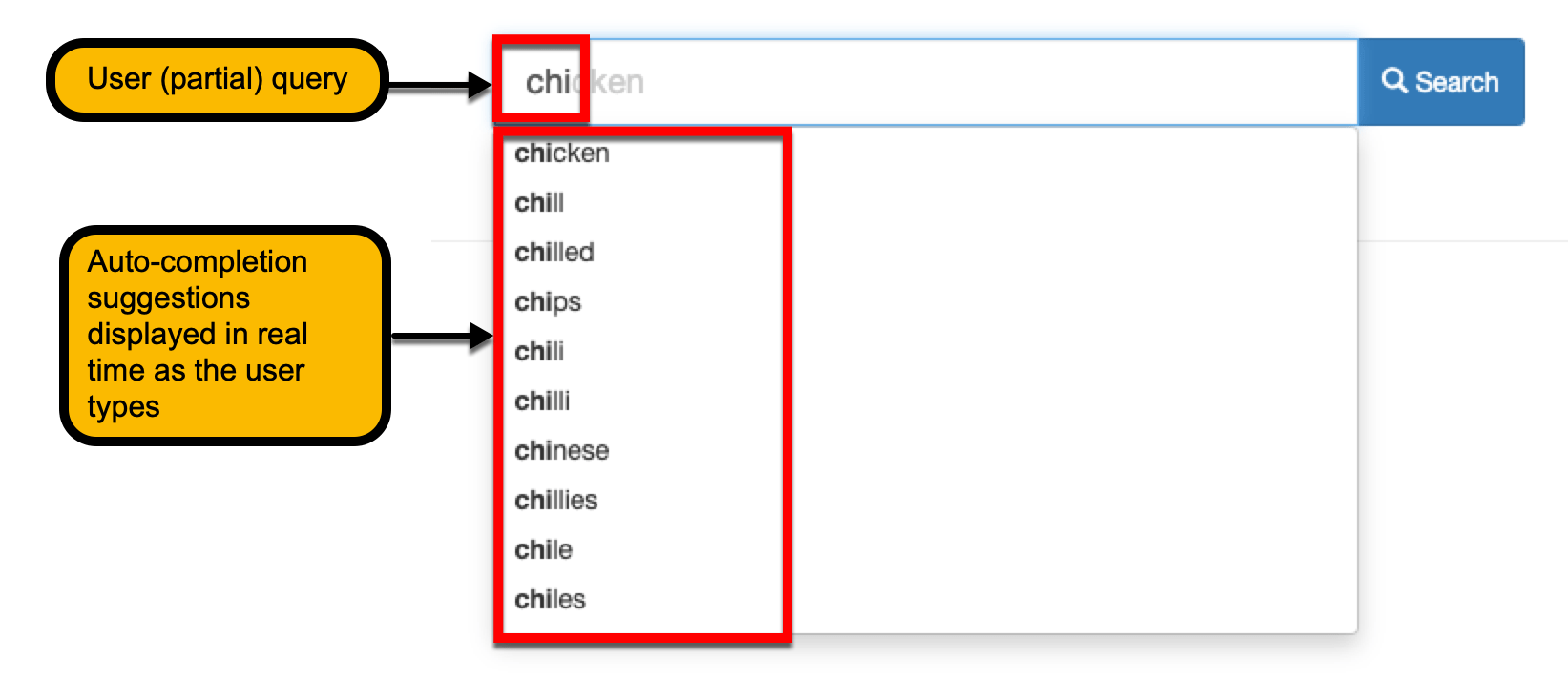
The suggestions presented by simple auto-completion are based off words and phrases found within the content that is being searched.
Clicking on the suggested term runs a search for the suggestion.
Structured auto-completion
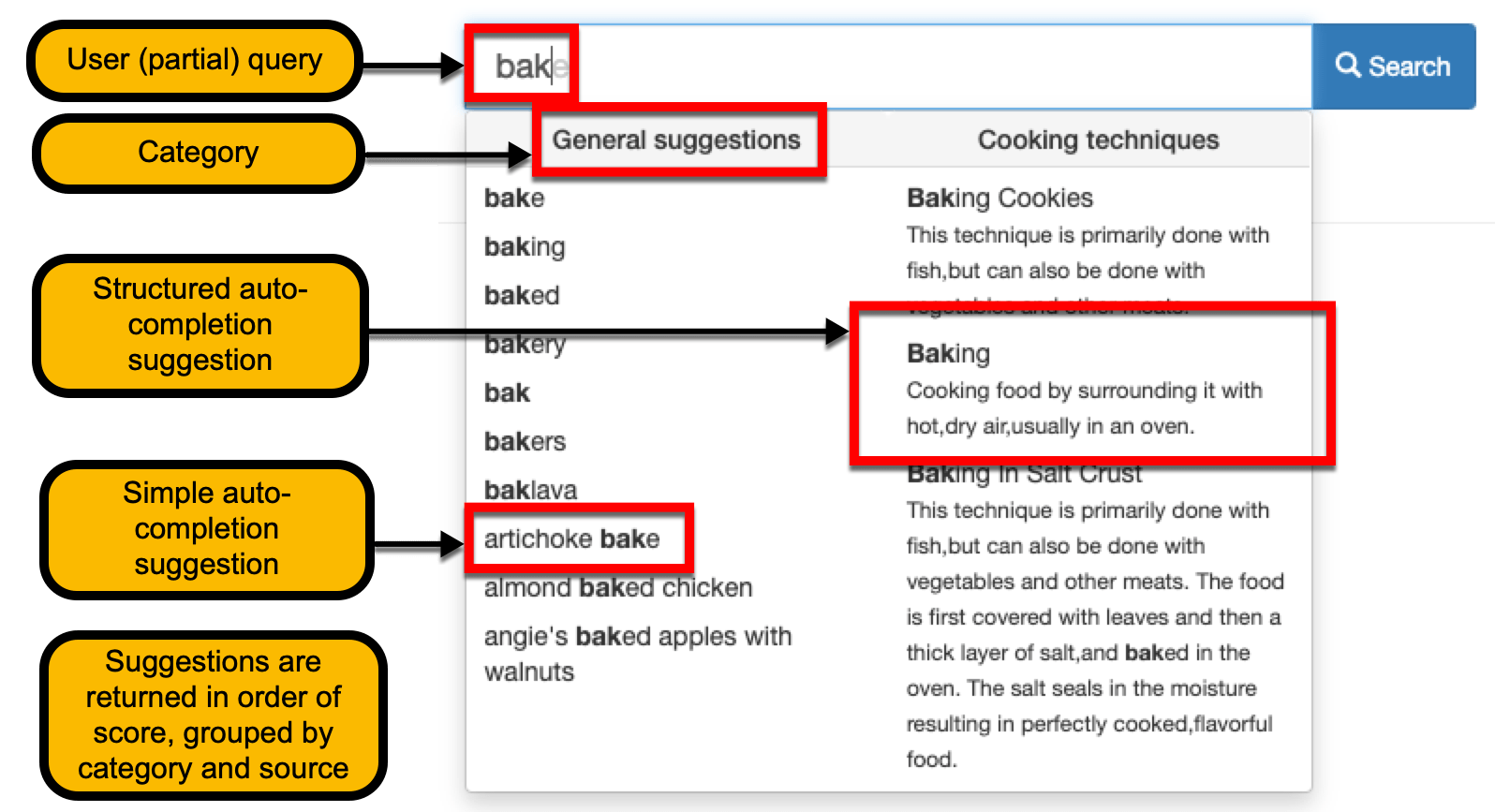
This provides advanced auto-completions based on structured data provided by the search administrator.
The suggestions can be grouped by an optional category value and provide rich content (such as thumbnail images and other data) to the users.
Clicking on a suggestion can do a number of things, depending on how the suggestion has been configured. It might:
-
Run a search (similar to simple auto-completion)
-
Take you directly to a page (like clicking on a search result)
-
Add some keywords to the search box
-
Display some results that you can’t click on (like information about a person in directory)
Search result summaries
Result set summary
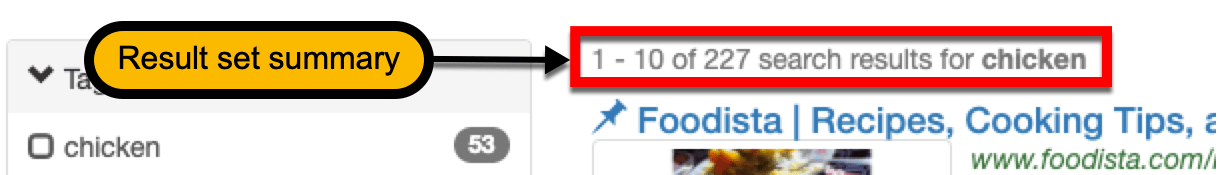
Once a search has been conducted via the search box, a results page for that search will be produced containing a number of search results.
A short summary of the set of results is returned along with the search results. This summary provides information about the number of results returned, which page of results is currently displayed and what was searched for.
Result item summary
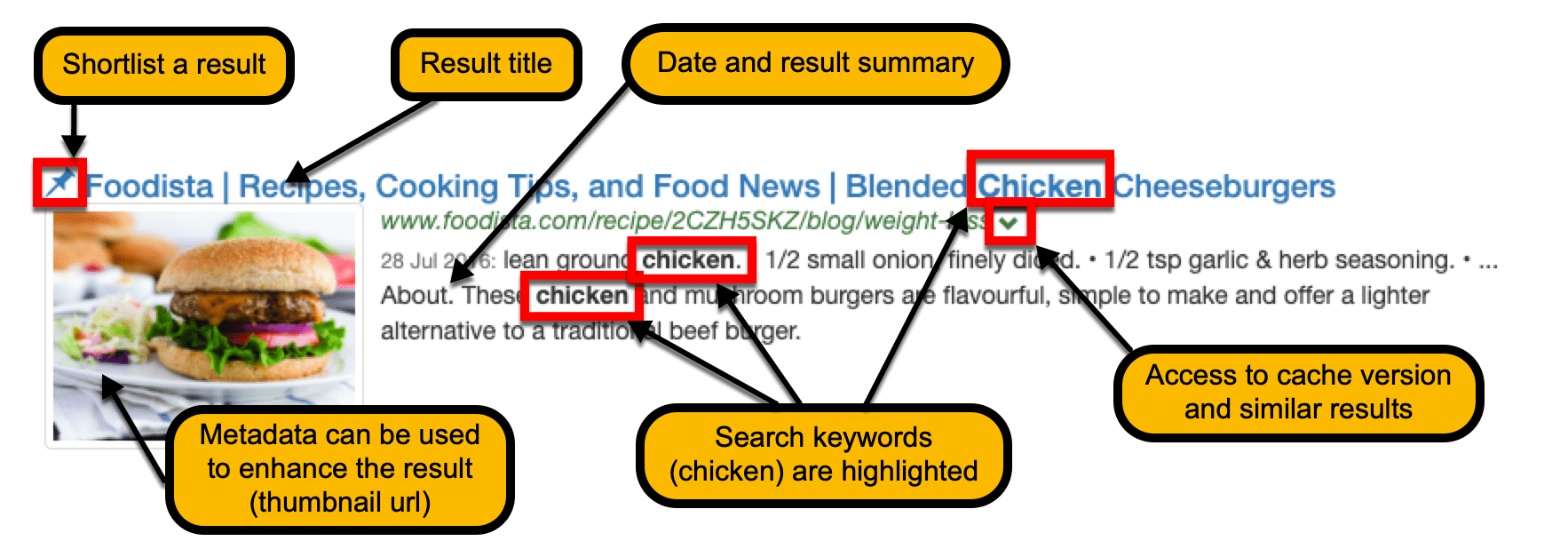
Each search result includes information about the result. This information will vary depending on what data is available and how the search has been configured. By default, the following is returned by Funnelback:
-
Linked title of the result item
-
URL of the item
-
Access to a cached version of the result
-
The date recorded for the result
-
A short summary of the result. This summary is usually automatically generated and centred around occurrences of the search terms within the context.
-
Indexed metadata can be used to enhance your search results - in this example the thumbnail URL is indexed as metadata and used to display the thumbnail image in the result template.
The keywords used by the user will always be highlighted in both the title, URL and result.
Search result filters (faceted navigation)
Faceted navigation provides search users with a set of filters that can be applied to narrow down a set of search results.
What is a facet?
A facet is best thought of as a way of filtering or segmenting the content within a website based on some property of the item. Each facet will include one or more facet categories which are the values of this item property.
For example a facet for color might be defined, with facet category values corresponding to individual colors (red, blue and so on).
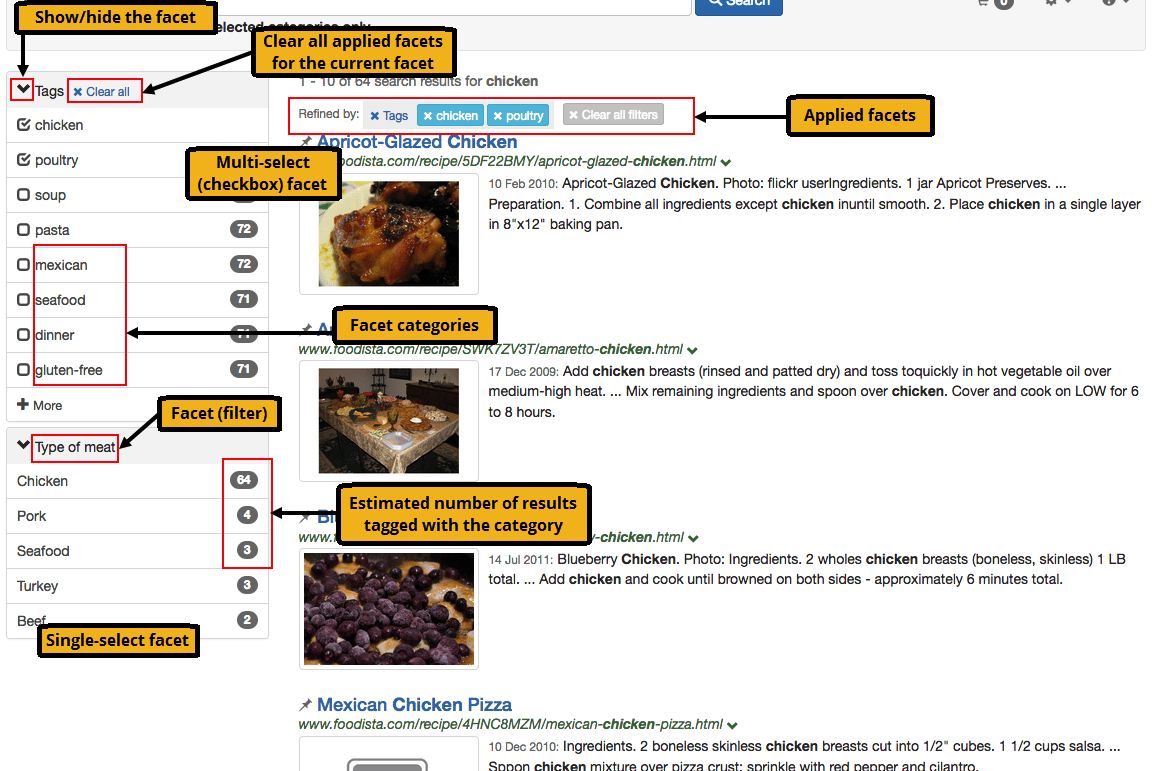
Configuration of faceted navigation relies on each item being tagged with the appropriate values that indicate the categories that apply for the item.
| The number of the results for each category within a facet are estimates only. |
Best bets
Best bets allows an administrator to configure a featured result item to be displayed when a user conducts a specific search.
A best bet is not a search result, but it can feature or promote a page / URL that is not part of a website that is being indexed.
For example, when a user searches for the term Foodista a best bet to featuring the Wikipedia page on Foodista wiki is displayed above the search results. This is presented in addition to the search results.
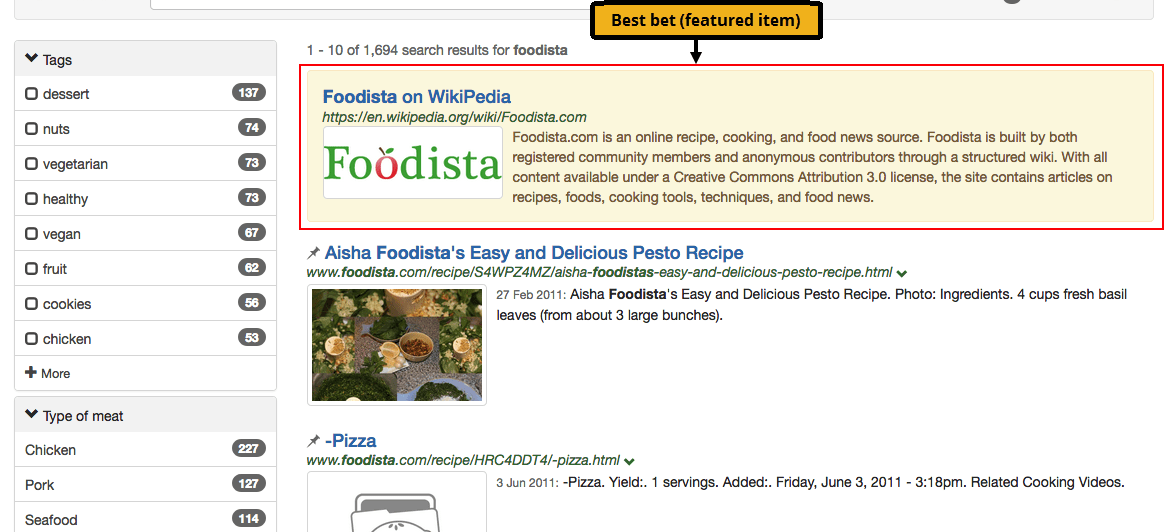
The style and appearance of the best bets in the search results is governed by the stylesheets that are applied to the search results template, and the position in the search results can be controlled by a search administrator with the ability to edit the templates. A best bet can include HTML formatting.
In the example above a HTML snippet including an image of the Foodista logo has been returned with the best bet.
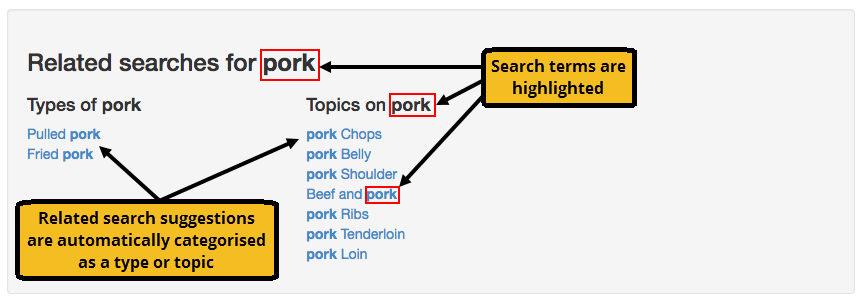
Related searches (contextual navigation)
Contextual navigation suggests a list of related searches by analyzing the result summaries in the set of results returned for a search.
These suggestions are grouped into types and topics related to the original search query.
For example, if a user performed a search for pork the related searches suggested may include types of pork such as pork chops and pork belly as well as topics on pork.
Clicking on a suggestion runs a proximity search for the suggested words. A proximity search looks for matching results where the suggested words are close to each other in the text.
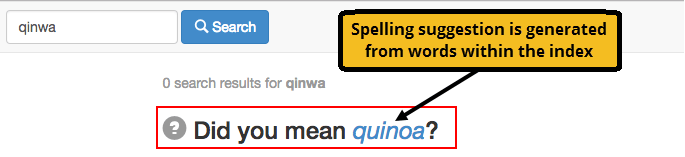
Spelling suggestions
Spelling suggestions sourced from words and phrases found in the content are automatically returned by Funnelback, regardless of if the search returns any results for the query.
Spelling suggestions when clicked will always return search results because they are based on words in the content and not an external dictionary.
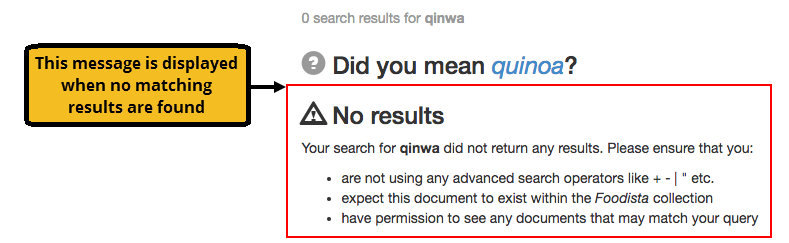
No results message
If a user enters a query that produces no results, a customizable no results message can be displayed. This message is customized via the design template of the search results page. The following is the default message:
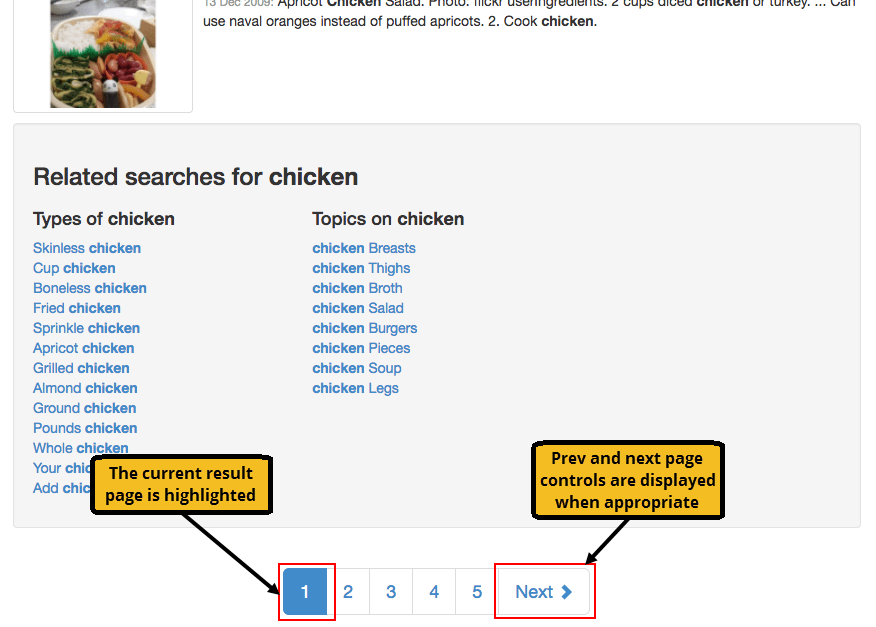
Pagination
The search results pagination control allows a user to page through the search results.
The control can be displayed multiple times (for example, above and below the search results) and can be customized by an administrator.
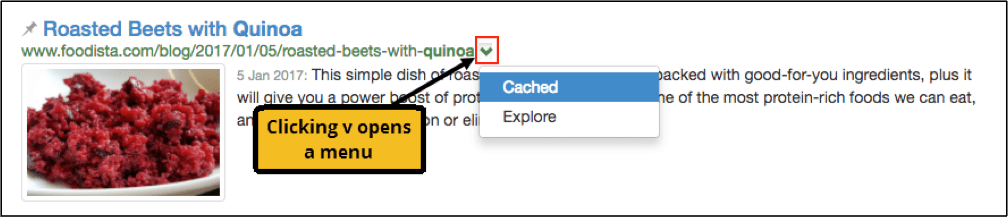
Cached results
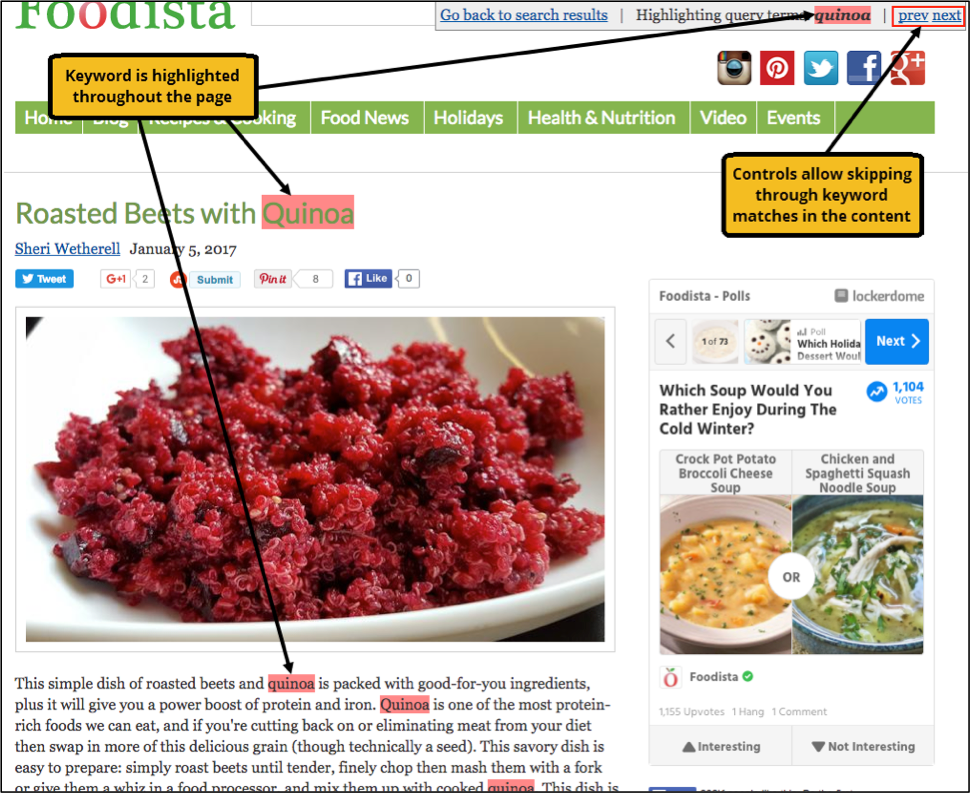
Every page that a search engine indexes is stored locally by Funnelback. This cached version of the page can be viewed from the search results, with the search query terms highlighted within the content. The cached version of a search result is accessed from the downward caret icon beside the URL of a search result.
Clicking this menu item opens a cached version of the page with the queried keywords highlighted within the content. The cached version is the content as it was when Funnelback crawled the URL. The example below shows the cached version of this result when the user searched for the keyword quinoa.
Search sessions and history
| The search sessions and history feature in Funnelback requires cookies to be enabled in the user’s browser. And therefore feature is only supported for Funnelback endpoints over HTTPS protocol. Funnelback has the ability to track a user’s search terms and recently visited items as well as providing the user with the ability to create a shortlist of search result items. |
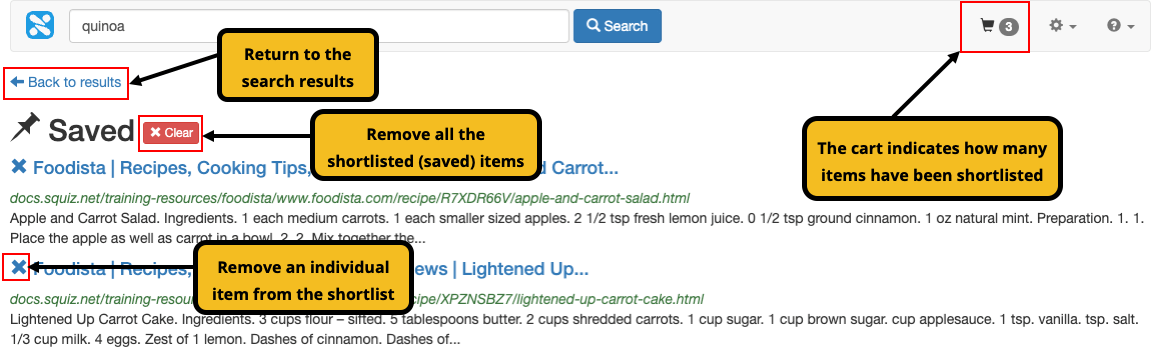
Result shortlisting
Result shortlisting provides a user with the ability to flag certain result items to be added to a shortlist (or result cart) by pinning the item. The pin changes to a cross once the item has been shortlisted. This allows a user to remove the item from the shortlist by clicking on the cross.

The shopping cart icon in the panel containing the search box shows how many items have been shortlisted. All the shortlisted items can also be viewed by clicking on the shopping cart icon.
Search history
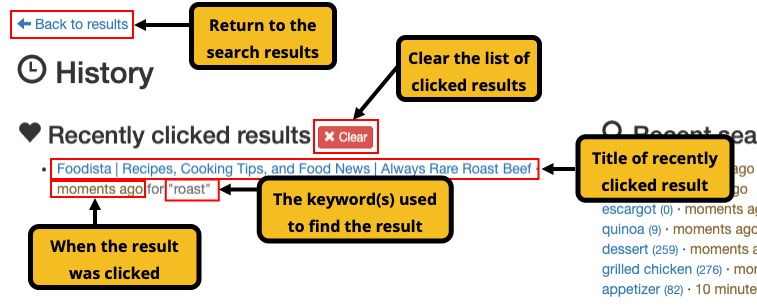
When search sessions are enabled a user’s search history is tracked as searches are submitted. A summary of the search history is displayed above the search results.

Additional information is displayed if you hover over an item. If the item has a filter applied (as indicated by the funnel icon) then the applied filters will display on hover, otherwise a tooltip indicating the time is displayed.

Clicking the more link opens the full history screen.
Visited items history
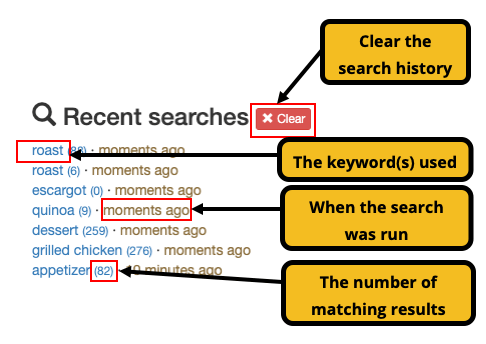
Funnelback also keeps track of all the search results that a user visits. Once a result has been visited an additional field is displayed within the result summary indicating the time that the visit occurred.

Clicking on the Last visited link also opens up the history screen which provides a full list of recently visited URLs.
Search result grouping (result collapsing)
Result collapsing groups similar search results together when displaying search results. The key or keys used for collapsing are configured by a search administrator and are based on either the documents content, or the document’s metadata.
For example, the result item below from a search of the complete works of Shakespeare shows that there are 21 very similar results to the Merchant of Venice: list of scenes result. This search has been configured to group or collapse all search results that are tagged with the same metadata value for a field recording the name of the play.

Clicking on the 21 very similar results lists the 22 search results that form part of this group (the list of scenes result plus the 21 similar results). These can be sorted by providing a sort parameter in your More… link or by setting -sort in your query processor options. The sort options for this list of similar results are the same as for any normal search result sort.
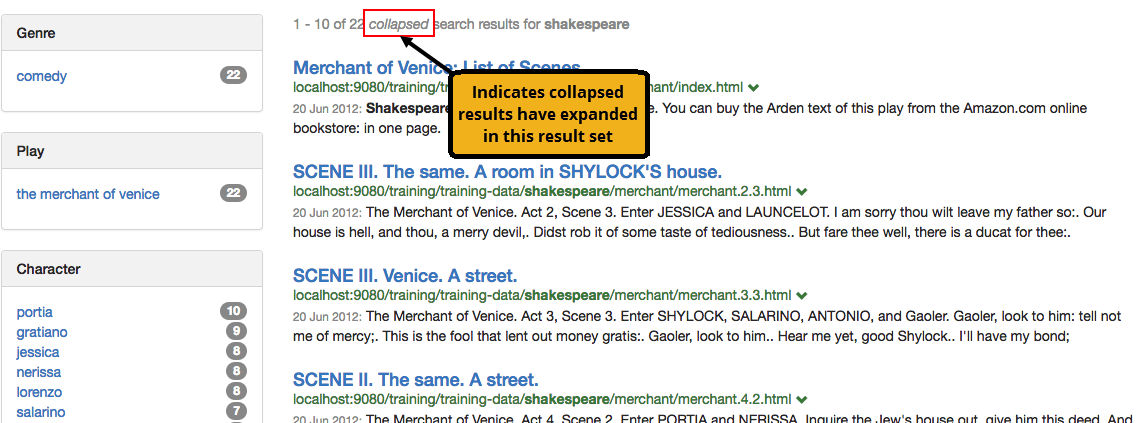
The initial search result can also be customized to show some additional information for the collapsed results.
The example result below, from another site groups sections of a publication together. The search result is configured to display the title of the first four collapsed items with a More… link which is the same as the 21 similar items link in the previous example.
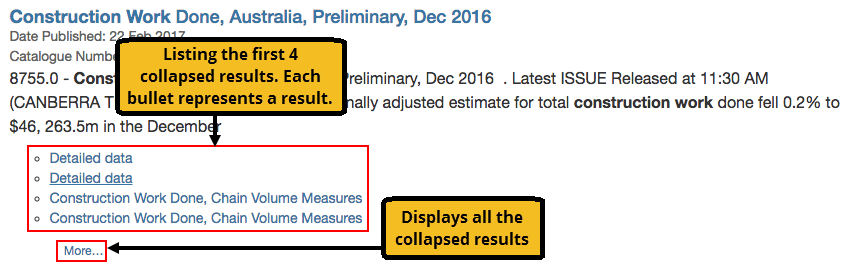
These (nested) collapsed results can be sorted using the -collapsed_docs_sort query processor option. This option will affect the set of collapsed results that are returned within the intial search response (controlled by the -collapsed_num_ranks option).
Quick links
Quick links are direct links to important sub-pages of a home page and can be displayed as part of the result summary. Quick links are normally only used when providing a multi-site search such as a whole of university search. The search result can also include an optional search box that restricted to the specific site displayed for the search result.
For example a search for the University of Sydney might produce the following search result. Entering a search into the search box will run a search restricted to pages from the Sydney Conservatorium of Music website.
